Mediport
A mediport, also known as a port-a-cath, is a small medical device implanted under the skin that provides easy access to a vein. This device is commonly used for patients who require frequent administration of medications, blood transfusions, chemotherapy, or blood draws. Below is essential information about mediport placement and care.
What is a Mediport?
A mediport consists of two main parts:
- The Port: A small reservoir with a silicone top that sits just beneath the skin.
- The Catheter: A thin, flexible tube that connects the port to a large vein, usually in the chest.
When needed, a special needle is inserted through the skin into the port to administer medications or draw blood.
Why Get a Mediport?
Mediports are often recommended for patients who need long-term or frequent intravenous (IV) treatments. They provide a more convenient and comfortable option compared to repeated needle sticks in the arms or hands.
Benefits of a Mediport:
- Reduces the need for multiple IV sticks
- Long-lasting (can remain for months or years)
- Decreases the risk of vein damage
The Mediport Placement Procedure
Mediport placement is a minor surgical procedure typically performed by an Interventional Radiologist, a specialized doctor who uses medical imaging to guide minimally invasive procedures. Here's what to expect:
Preparation:
-The procedure is usually done under local anesthesia with sedation to keep you relaxed.
-Your interventional radiologist may use ultrasound or X-ray imaging to locate the best vein for catheter placement.Procedure:
-A small incision is made near your collarbone or chest.
-The port is placed under the skin, and the catheter is threaded into a large vein (often the superior vena cava).
-The entire process is guided by imaging to ensure accurate placement.
-The incision is closed with sutures or surgical glue.After Placement:
-You may experience some discomfort or bruising around the incision site.
-A dressing will be applied to protect the area while it heals.
-Your healthcare provider will give you instructions on how to care for the incision site.
Aftercare and Living with a Mediport
After the placement of your mediport, caring for it is relatively simple. Here are some key points:
Site Care:
-Keep the incision area clean and dry until it heals.
-Watch for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage. Contact your healthcare provider if these symptoms occur.Using the Mediport:
-Only trained medical professionals should access the mediport using a special needle.
-The port may be flushed with saline to keep it open between uses.Daily Life:
-You can resume most of your regular activities after healing, but avoid strenuous exercises involving the chest.
-Be mindful of your mediport when wearing seatbelts, bras, or carrying bags.Infection Prevention:
-Always ensure proper hygiene when your mediport is accessed.
-Inform your healthcare provider if you develop a fever or chills, as these could be signs of an infection.
When to Call Your Doctor
- Pain or swelling at the port site
- Difficulty breathing or swelling in the arm or neck
- Fever or chills
- Fluid leaking from the incision site
Removing the Mediport
Mediports are removed once they are no longer needed. The removal procedure is usually simple and can often be done under local anesthesia by the same interventional radiologist or another trained healthcare provider. A small incision is made to remove the port and catheter, and the wound is closed.
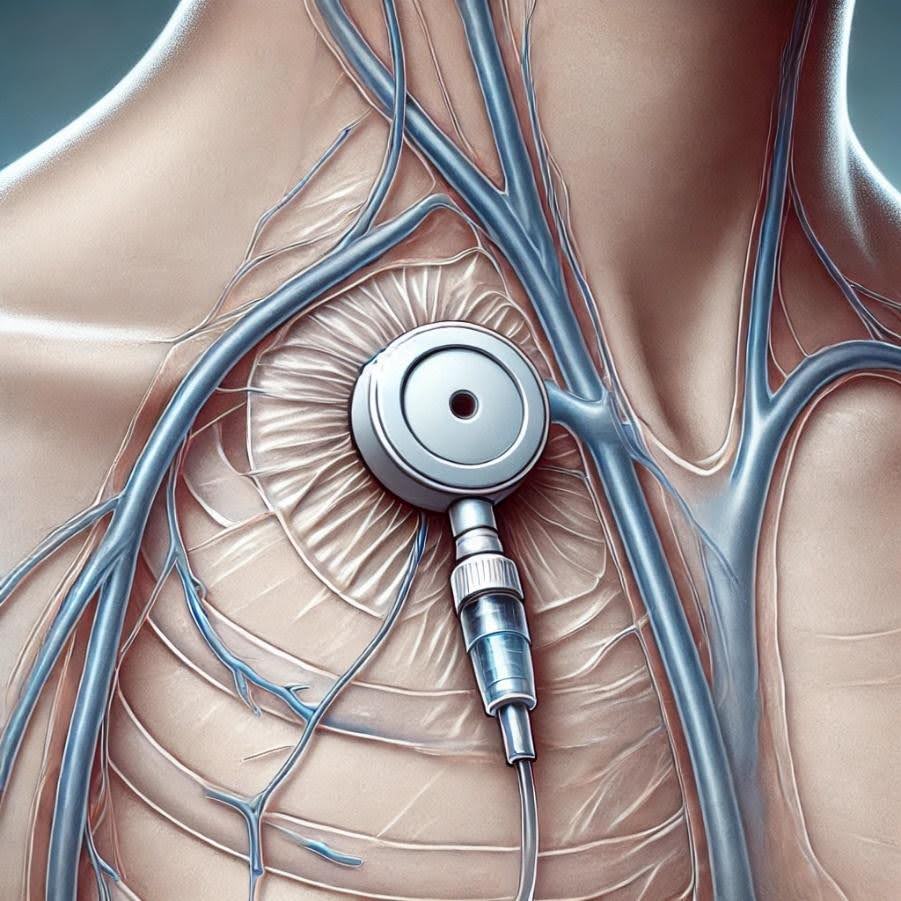
Image generated by AI
Print PageContact us to request an appointment or ask a question. We're here for you.



