Epididymitis
Epididymitis is a term used to describe inflammation of the epididymis. The epididymis is part of the male anatomy, a picture of which is shown.
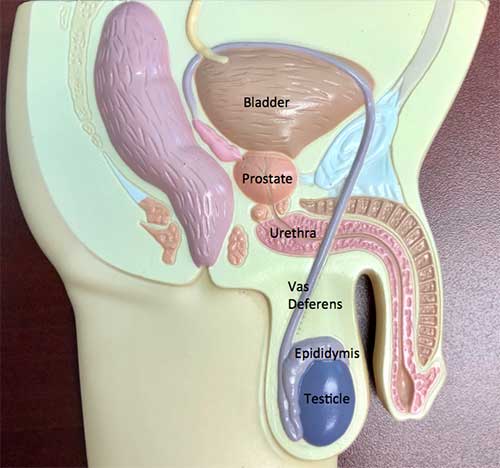
The scrotum, or sac, contains a testicle on each side. The testicle has two functions. It makes testosterone, the male hormone, which is absorbed into the blood stream. It also makes sperm, which travels from the testicle into a series of tubes which collectively form the epididymis. The epididymis sits to the side and in back of the testis. Sperm leaves the epididymis by way of the vas deferens (this is the tube that is divided during a vasectomy) which travels to join the seminal vesicles and prostate. Sperm mixes with fluid from the seminal vesicles and prostate to produce the semen, the fluid that comes out from the penis at the time of ejaculation.
Inflammation of the epididymis can occur due to a variety of causes, some of which include urinary infection, viral illness elsewhere in the body, minor physical trauma and reaction to medication.
Causes of Epididymitis
In many cases, the exact cause of an episode of epididymitis may not be identified. During examination, the physician checks to make sure other problems are not present which can also cause scrotal pain, such as testicular tumor, hernia, or varicocele. In some cases, a scrotal ultrasound may be recommended.
How is Epididymitis Treated?
Epididymitis is typically treated with hot Sitz baths, scrotal support, anti-inflammatory medication and occasionally antibiotics. Sitting in a warm tub for 20 minutes a day helps lessen inflammation. Scrotal support, with an athletic supporter or tight jockey style underwear, lessens the tension of the spermatic cord. Anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil or Nuprin) at doses of 400-600 mg, 3 times a day can provide pain relief and reduce swelling. Antibiotics are to be used if directed by your doctor.
Epididymitis may take 2-4 weeks to resolve. If symptoms persist beyond that, reexamination is indicated.
Occasionally, epididymitis becomes chronic in nature. Treatment of this condition is more difficult. Sometimes a “block” of the spermatic cord is carried out by injecting a mixture of Novocain and cortisone into the groin area. Rarely, surgical removal of the epididymis may be necessary (a procedure called epididymectomy).
In most cases, epididymitis can be treated very effectively, and most men can be relieved of their symptoms.
Print PageContact us to request an appointment or ask a question. We're here for you.




